【漏洞预警】Wordpress内容注入漏洞致超67000个网站遭黑产利用
作者:admin | 时间:2017-2-9 13:25:40 | 分类:黑客技术 隐藏侧边栏展开侧边栏

受最新WordPress的漏洞影响超过67000个网站被攻击
如果你的网站使用的是WordPress,并且没有及时更新官方上周发布的补丁,升级到v4.7.2版本,那么你的网站很有可能受到这4个黑客组织的攻击。
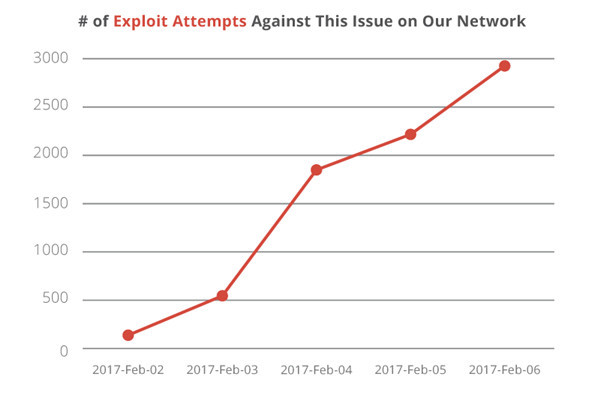
据国外Web安全公司Sucuri表示,自上周一该漏洞细节公开后,攻击范围不断扩大,最近每天趋于3000次。
随着时间的推移利用REST API漏洞尝试次数(来源:Sucuri)
攻击者正在利用WordPress的REST API的漏洞,该漏洞由WordPress团队两个星期前修复并更新补丁,他们于上周一公开了漏洞详情。
攻击者利用这个漏洞精心构造一个向目标站点REST API发起的HTTP请求,可以修改文章的标题和内容。
上周已经有人提供了完整的利用代码。
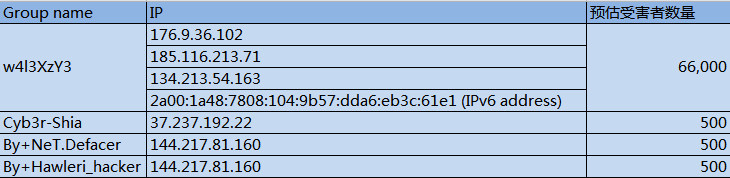
超过67,000的网站内容已经被篡改
即使该漏洞仅影响WordPress4.7.0和4.7.1两个版本而且该CMS内置有自动更新的功能,但仍然有很多网站没有更新。
据Sucuri部署的蜜罐服务器收集到的数据显示,在过去的一周,有四波攻击者正在着手利用这个漏洞。
由于攻击已经持续一段时间了,谷歌已经可以检索一部分被攻击的内容。
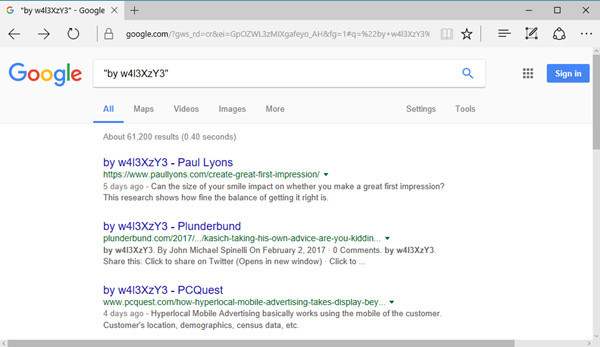
通过Google检索被篡改的站点
通过Google搜索"by w4l3XzY3",可以浏览一些受影响的站点。
部分受影响的站点列表
更多受影响站点可在http://www.zone-h.org/archive/notifier=w4l3XzY3/page=1查看。
目前,使用REST API漏洞篡改网站的这些组织只是做了一些知名度的曝光,将网站内文章的标题和正文修改为自己的内容。
其中一个被篡改的站点
Sucuri's CTO, Daniel Cid表示希望看到更专业的内容进入大家的视野,如利用该漏洞发布更复杂的内容,黑链SEO:如插入链接和图像。
利用漏洞做这种篡改的话,做黑链SEO,可以提高其他网站的搜索引擎排名,或者宣传一些其他的非法产品。
当然如果网站内容被篡改为一些恶意内容,会导致网站被搜索引擎屏蔽。
建议所有使用WordPress的网站主及时更新至最新版本v4.7.2。避免由于REST API的安全问题,导致网站被搜索引擎屏蔽。
WordPress REST API 内容注入漏洞分析(漏洞分析内容转载自:http://paper.seebug.org/208/)
0x00 漏洞简述
1. 漏洞简介
在REST API自动包含在Wordpress4.7以上的版本,WordPress REST API提供了一组易于使用的HTTP端点,可以使用户以简单的JSON格式访问网站的数据,包括用户,帖子,分类等。检索或更新数据与发送HTTP请求一样简单。上周,一个由REST API引起的影响WorePress4.7.0和4.7.1版本的漏洞被披露,该漏洞可以导致WordPress所有文章内容可以未经验证被查看,修改,删除,甚至创建新的文章,危害巨大。
2. 漏洞影响版本
WordPress4.7.0
WordPress4.7.1
0x01 漏洞复现
Seebug上已经给出详细的复现过程,在复现过程中可以使用已经放出的POC来进行测试。
0x02 漏洞分析
其实漏洞发现者已经给出了较为详细的分析过程,接下来说说自己在参考了上面的分析后的一点想法。
WP REST API
首先来说一下REST API。
控制器
WP-API中采用了控制器概念,为表示自愿端点的类提供了标准模式,所有资源端点都扩展WP_REST_Controller来保证其实现通用方法。
五种请求
之后,WP-API还有这么几种请求(也可以想成是功能吧):
HEAD
GET
POST
PUT
DELETE
以上表示HTTP客户端可能对资源执行的操作类型。
HTTP客户端
WordPress本身在WP_HTTP类和相关函数中提供了一个HTTP客户端。用于从另一个访问一个WordPress站点。
资源
简单来说,就是文章,页面,评论等。
WP-API允许HTTP客户端对资源执行CRUD操作(创建,读取,更新,删除,这边只展示和漏洞相关的部分):
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/posts获取帖子的集合:
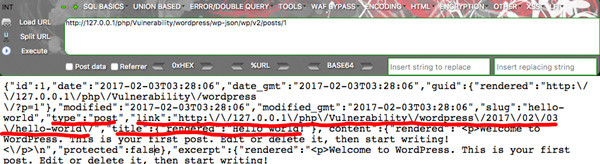
GET /wp-json/wp/v2/posts/1获取一个ID为1的单独的Post:
可以看到ID为1的文章标题为Hello World,包括文章的路由也有。
路由
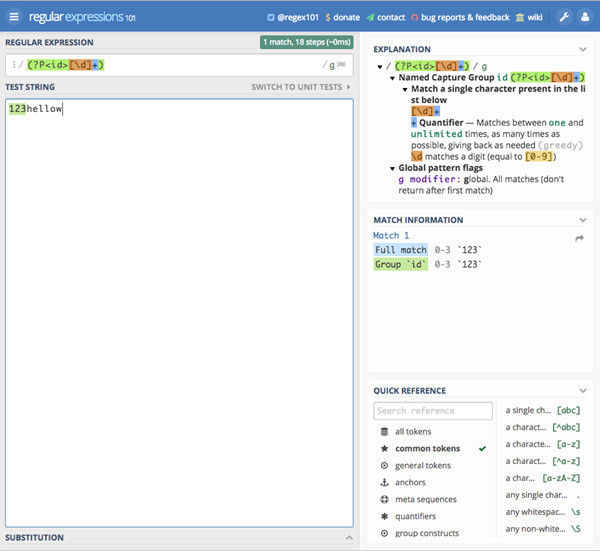
路由是用于访问端点的“名称”,在URL中使用(在非法情况下可控,就像这个漏洞一样)。
例如,使用URLhttp://example.com/wp-json/wp/v2/posts/123:
路由(route)是wp/v2/posts/123,不包括wp-json,因为wp-json是API本身的基本路径。
这个路由有三个端点:
GET触发一个get_item方法,将post数据返回给客户端。
PUT触发一个update_item方法,使数据更新,并返回更新的发布数据。
DELETE触发delete_item方法,将现在删除的发布数据返回给客户端。
静态追踪
知道了WP-API的路由信息以及其操作方式,可以根据其运行的思路来看一下具体实现的代码。
我们看一下/wp-includes/rest-api/endpoints/class-wp-rest-post-controller.php:
根据上面的信息,我们可以知道这是注册controller对象的路由,实现路由中端点方法。
在这里,如果我们向/wp-json/wp/v2/posts/1发送请求,则ID参数将被设置为1:
同时,注意一下这里:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
register_rest_route( $this->namespace, '/' . $this->rest_base . '/(?P<id>[\d]+)', array(
array(
'methods' => WP_REST_Server::READABLE,
'callback' => array( $this, 'get_item' ),
'permission_callback' => array( $this, 'get_item_permissions_check' ),
'args' => $get_item_args,
),
array(
'methods' => WP_REST_Server::EDITABLE,
'callback' => array( $this, 'update_item' ),
'permission_callback' => array( $this, 'update_item_permissions_check' ),
'args' => $this->get_endpoint_args_for_item_schema( WP_REST_Server::EDITABLE ),
),
array(
'methods' => WP_REST_Server::DELETABLE,
'callback' => array( $this, 'delete_item' ),
'permission_callback' => array( $this, 'delete_item_permissions_check' ),
'args' => array(
'force' => array(
'type' => 'boolean',
'default' => false,
'description' => __( 'Whether to bypass trash and force deletion.' ),
),
),
),
'schema' => array( $this, 'get_public_item_schema' ),
) );
|
可以看到在register_rest_route中对路由进行了正则限制:
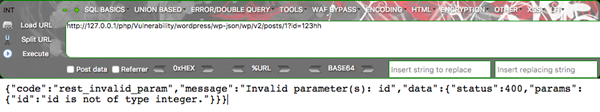
也就是防止攻击者恶意构造ID值,但是我们可以发现$_GET和$_POST值优先于路由正则表达式生成的值:
这边没有找到ID为123hh的项目,所以返回rest_invalid。
现在我们可以忽略路由正则的限制,来传入我们自定义的ID。
接下来在审查各个端点方法中,找到了update_item这个方法,及其权限检查方法update_item_permissions_check:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public function update_item_permissions_check( $request ) {
$post = get_post( $request['id'] );
$post_type = get_post_type_object( $this->post_type );
if ( $post && ! $this->check_update_permission( $post ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_edit', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to edit this post.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! empty( $request['author'] ) && get_current_user_id() !== $request['author'] && ! current_user_can( $post_type->cap->edit_others_posts ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_edit_others', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to update posts as this user.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! empty( $request['sticky'] ) && ! current_user_can( $post_type->cap->edit_others_posts ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_assign_sticky', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to make posts sticky.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
if ( ! $this->check_assign_terms_permission( $request ) ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_cannot_assign_term', __( 'Sorry, you are not allowed to assign the provided terms.' ), array( 'status' => rest_authorization_required_code() ) );
}
return true;
}
|
可以看到,此函数通过检查文章是否实际存在,以及我们的用户是否有权限编辑这边文章来验证请求。但是当我们发送一个没有响应文章的ID时,就可以通过权限检查,并允许继续执行对update_item方法的请求。
具体到代码,就是让$post为空,就可以通过权限检查,接下来跟进get_post方法中看一下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
function get_post( $post = null, $output = OBJECT, $filter = 'raw' ) {
if ( empty( $post ) && isset( $GLOBALS['post'] ) )
$post = $GLOBALS['post'];
if ( $post instanceof WP_Post ) {
$_post = $post;
} elseif ( is_object( $post ) ) {
if ( empty( $post->filter ) ) {
$_post = sanitize_post( $post, 'raw' );
$_post = new WP_Post( $_post );
} elseif ( 'raw' == $post->filter ) {
$_post = new WP_Post( $post );
} else {
$_post = WP_Post::get_instance( $post->ID );
}
} else {
$_post = WP_Post::get_instance( $post );
}
if ( ! $_post )
return null;
|
从代码中可以看出,它是用wp_posts中的get_instance静态方法来获取文章的,跟进wp_posts类,位于/wp-includes/class-wp-post.php中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public static function get_instance( $post_id ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_numeric( $post_id ) || $post_id != floor( $post_id ) || ! $post_id ) {
return false;
}
|
可以看到,当我们传入的ID不是全由数字字符组成的时候,就会返回false,也就是返回一个不存在的文章。从而get_post方法返回null,从而绕过update_item_permissions_check的权限检测。
回头再看一下可执行方法upload_item:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public function update_item( $request ) {
$id = (int) $request['id'];
$post = get_post( $id );
if ( empty( $id ) || empty( $post->ID ) || $this->post_type !== $post->post_type ) {
return new WP_Error( 'rest_post_invalid_id', __( 'Invalid post ID.' ), array( 'status' => 404 ) );
}
$post = $this->prepare_item_for_database( $request );
if ( is_wp_error( $post ) ) {
return $post;
}
// convert the post object to an array, otherwise wp_update_post will expect non-escaped input.
$post_id = wp_update_post( wp_slash( (array) $post ), true );
|
在这边将ID参数装换为一个整数,然后传递给get_post。而PHP类型转换的时候回出现这样的情况:
所以,也就是说,当攻击者发起/wp-json/wp/v2/posts/1?id=1hhh请求时,便是发起了对ID为1的文章的请求。下面为利用[exploit-db][2]上的POC来进行测试:
新建文章:
测试:
测试结果:
多想了一下
乍一看,感觉这个洞并没有什么太大的影响,但是仔细想了一下,危害还是很大的。先不说WordPress页面执行php代码的各种插件,还有相当一部分的WordPress文章可以调用短代码的方式来输出特定的内容,以及向日志中添加内容,这是一个思路。
另一个思路就是可以进行对原来文章中的指定超链接进行修改,从而进行钓鱼。
还有一个思路,就是利用WordPress文章中解析html以及JavaScript文件包含的做法,辅助其他方法,进行攻击。
0x03 diff比较
对于该漏洞,关键的修改在/wp-includes/class-wp-post.php中:
更改了对于$post_id的参数的传入顺序和判断条件,防止了我们传入数字+字母这样的格式进行绕过。
0x04 修补方案
将WordPress更新到最新版本。
0x05 参考链接
https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-92637
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/41223/
https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html
本文转载自 Paper